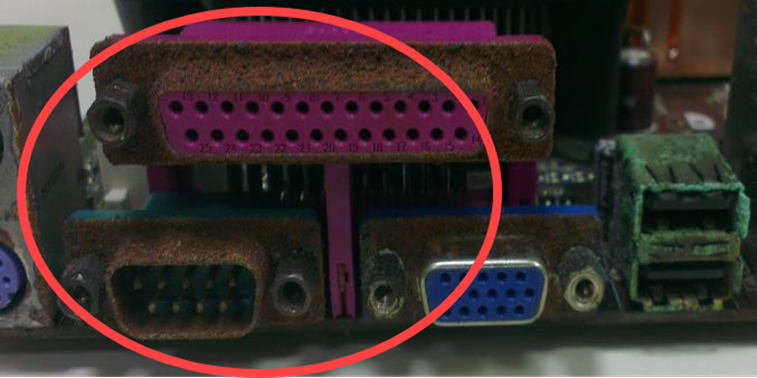
[MiniPC/NUC/AIOT Embedded] Customer Induced Damage (CID) Criteria
ASUS does not warrant uninterrupted or error-free operation of this Product. The warranty only covers technical hardware issues during the Warranty Period and in normal use conditions. If damage is caused by the following factors, warranty service will not be provided.
For more warranty information, please refer to the ASUS Product Warranty Card.
Note: ASUS authorized service centers may offer services for replacing CID (Customer Induced Damage) parts. If a customer requests CID repairs, both parts and labor will be charged. For more information, please contact an ASUS authorized service center.
Note: The list below is not exhaustive, and the example images are for illustrative purposes only and are for reference only. For more information, please contact an ASUS authorized service center.
Motherboard
Liquid intrusion and water stains on the Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
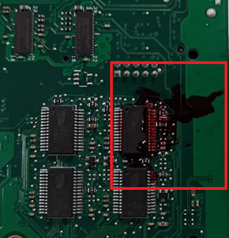
Oxidation on the Printed Circuit Board (PCB), such as verdigris
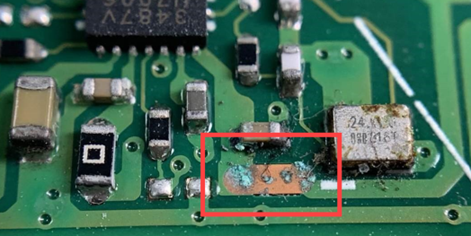
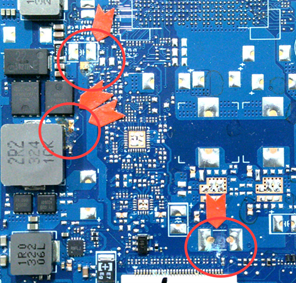
Rust or Corrosion on the Printed Circuit Board (PCB)




Deformation or warping of the Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
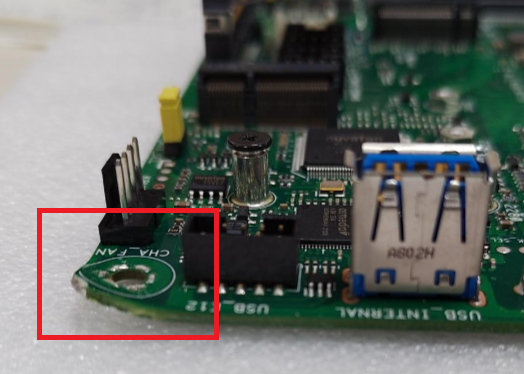
Cracks or damage to the Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
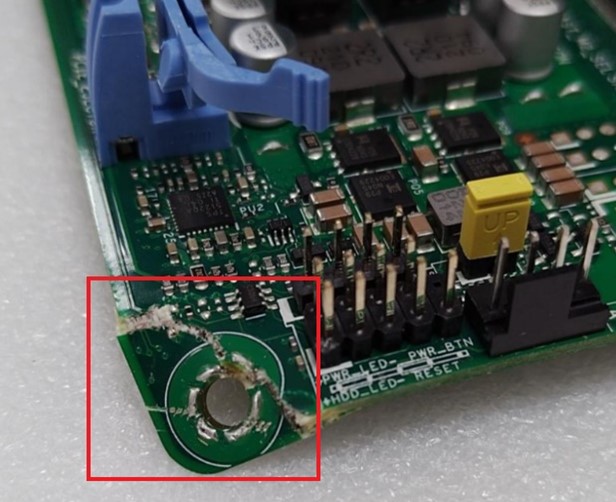
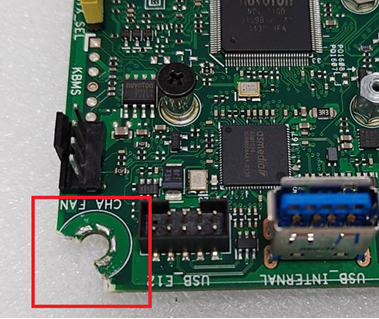


Scratches or abrasions on the Printed Circuit Board (PCB) surface, affecting solder points, copper tracks, traces, or screw holes
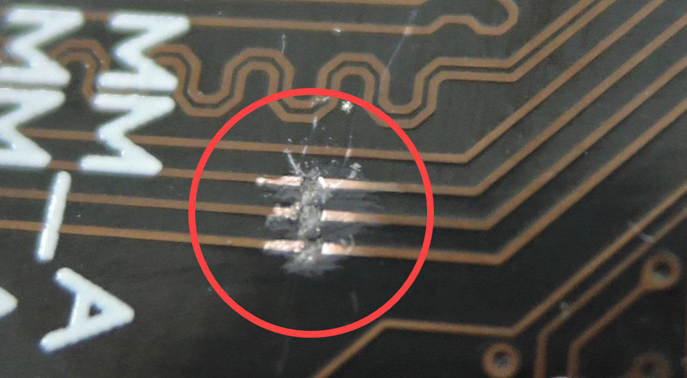
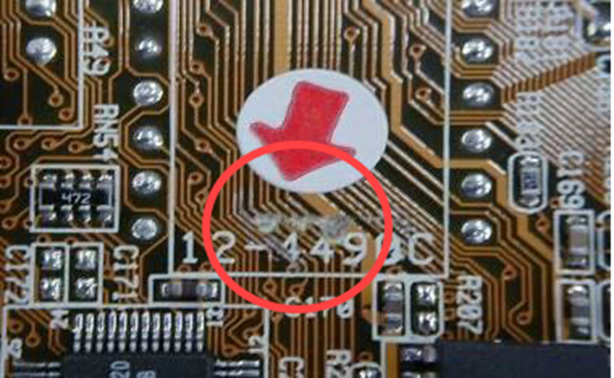
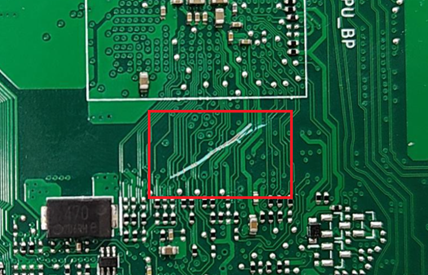

Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Scratched (Applicable only to the positions of the solid-state drive or memory)
Slight scratches are observed on the circuit board within the memory and solid-state drive installation zones. Furthermore, these slight surface abrasions on the circuit board do not exceed 20 millimeters in length, and the scratches have not resulted in damage to the copper foil, traces, or components.
Note: If the device is still under warranty and the scratch does not affect the functionality, then it is covered by the warranty.
Damage to components on the Printed Circuit Board (PCB), including misalignment or incorrect parts, detachment, or absence
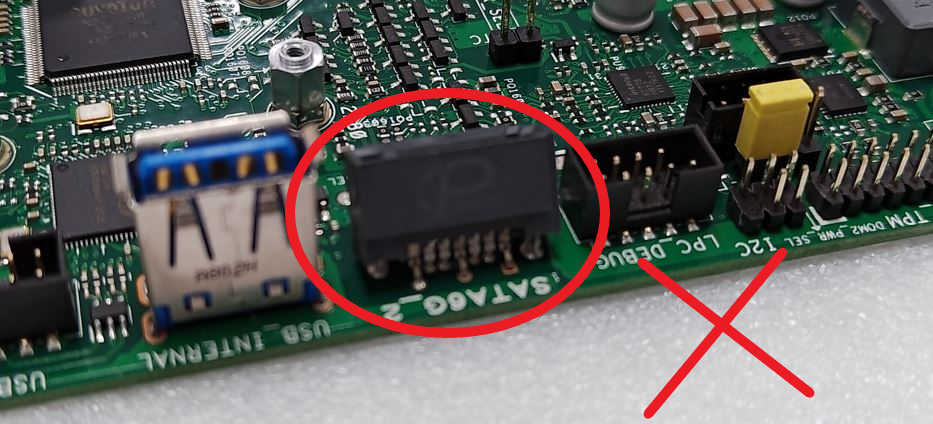
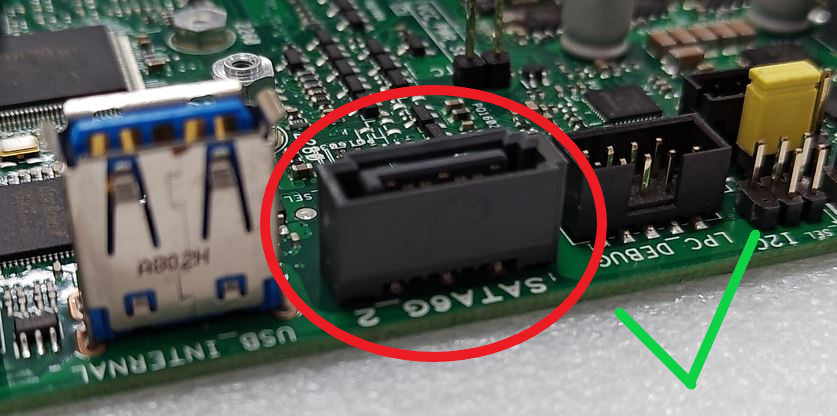
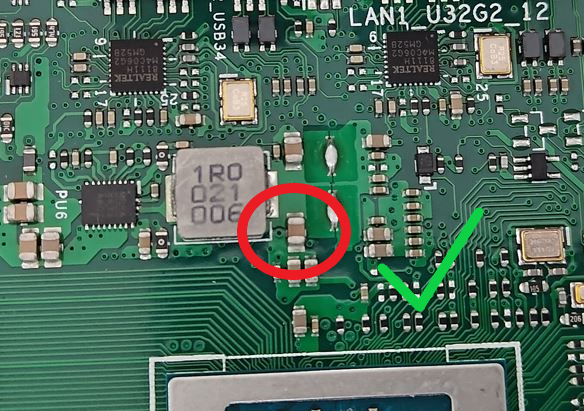




Damage, detachment, or absence of soldered components on the Printed Circuit Board (PCB)

Connector damage, detachment, or absence on the Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
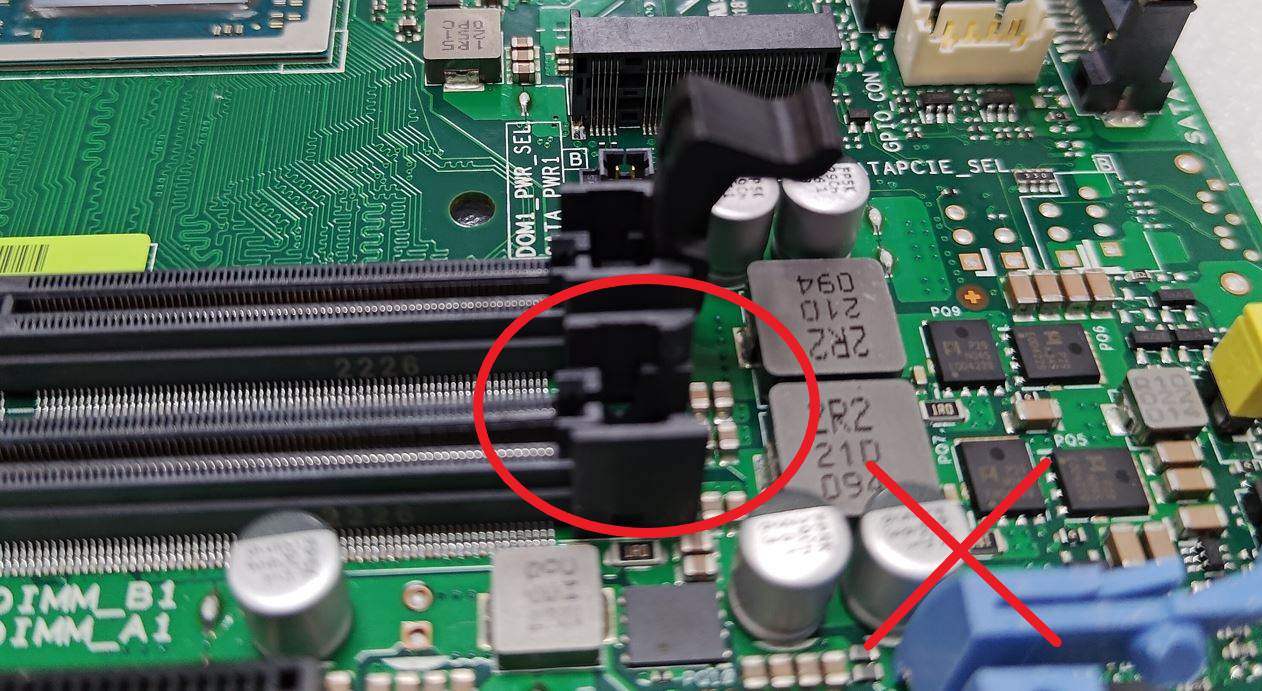
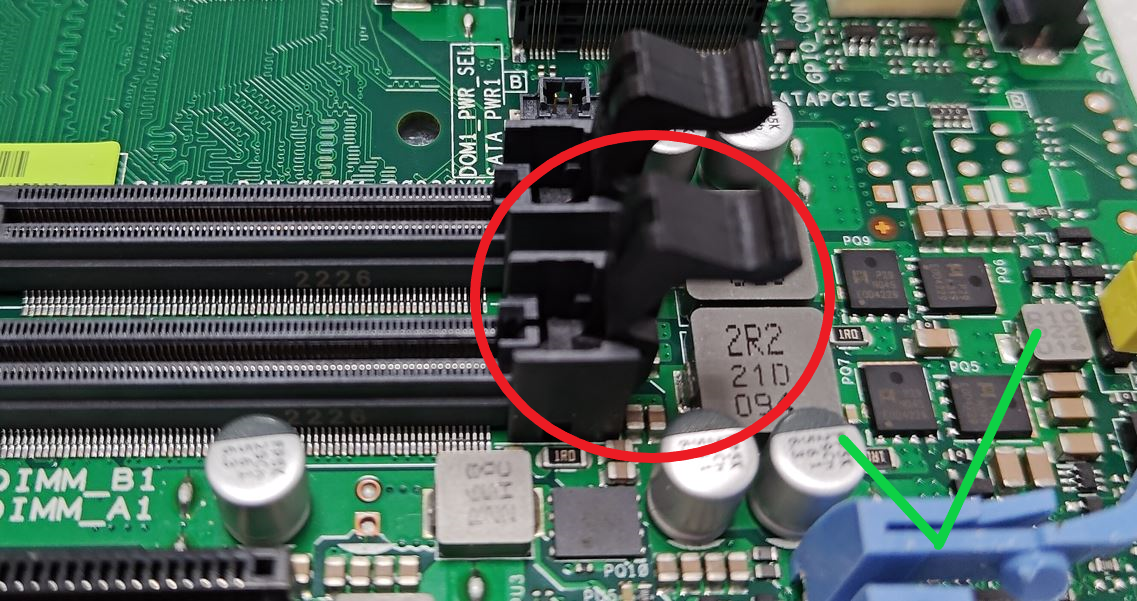
Jumper wires on the Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
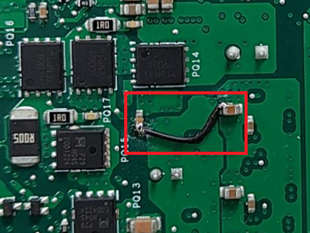

Bent or damaged CPU pins/CPU socket on the motherboard
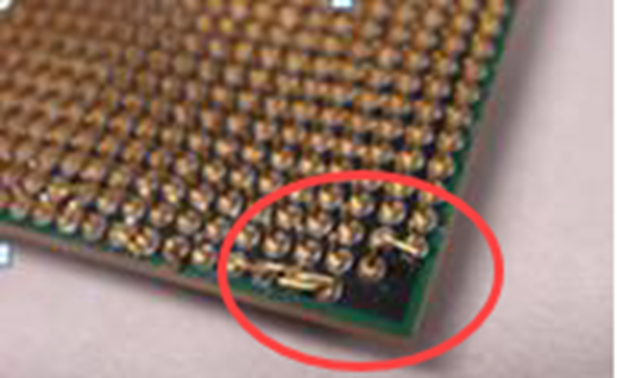
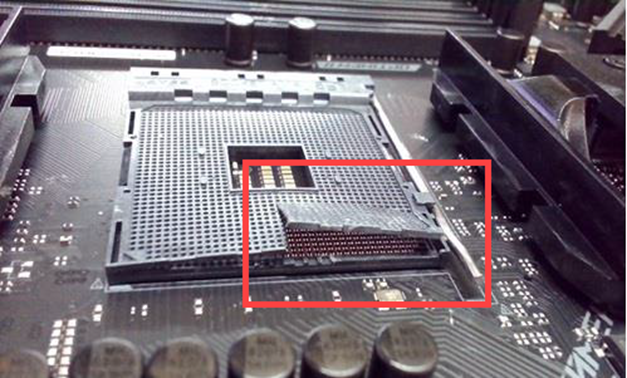
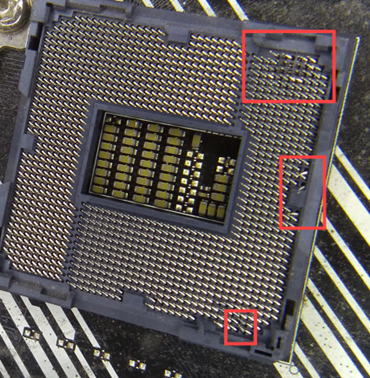

Power Supply (Adapter)
Power supply casing is deformed or damaged

Power supply cables are damaged or broken
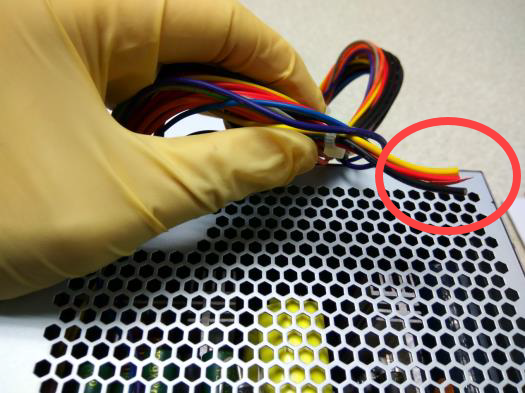
Power supply casing is rusted and moldy


Separation or deformation of the adapter casing
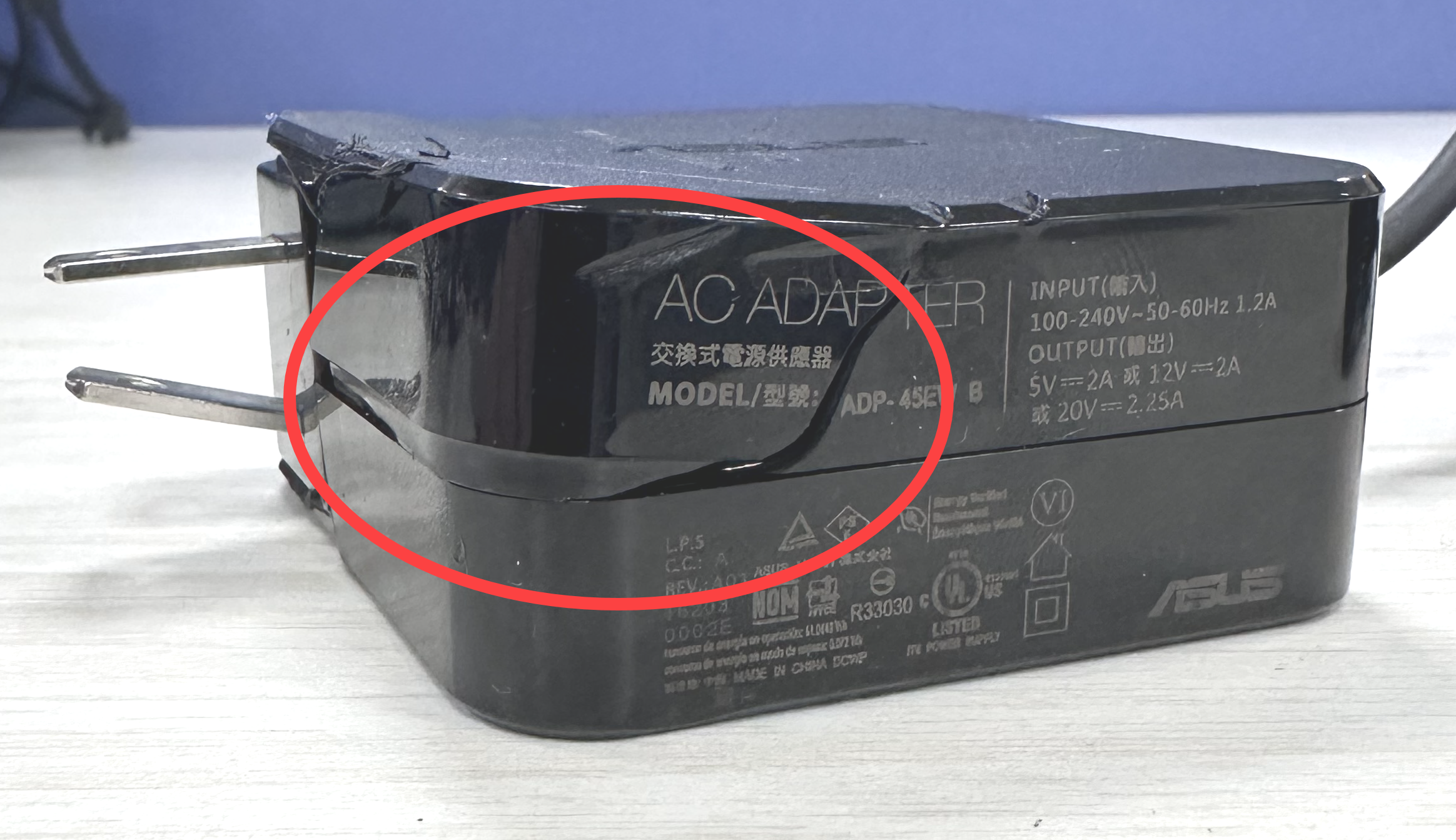
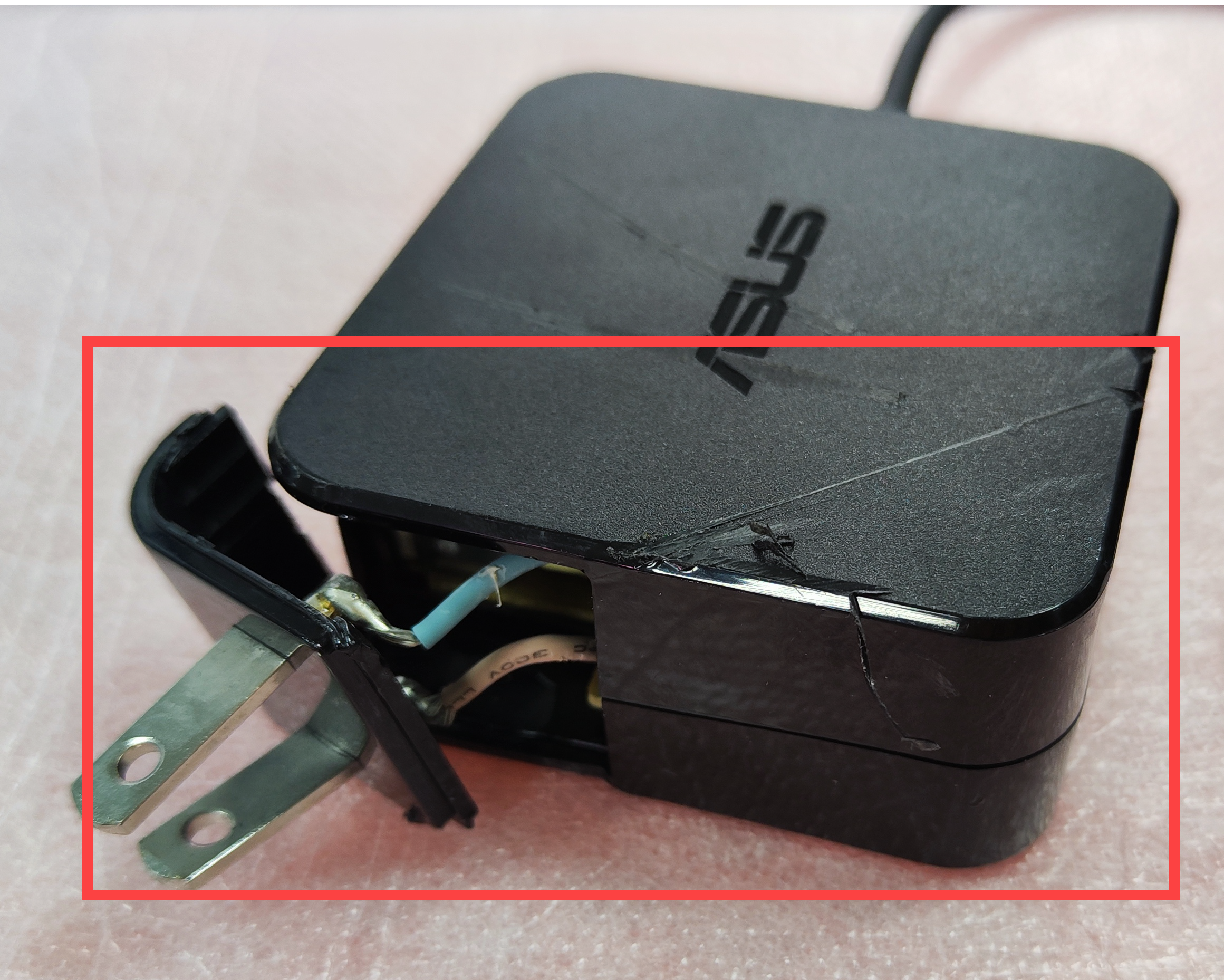

Damage or breakage to the adapter cables
Oxidation to the adapter connectors

Thermal Module
Damage or breakage to the fan module/blades
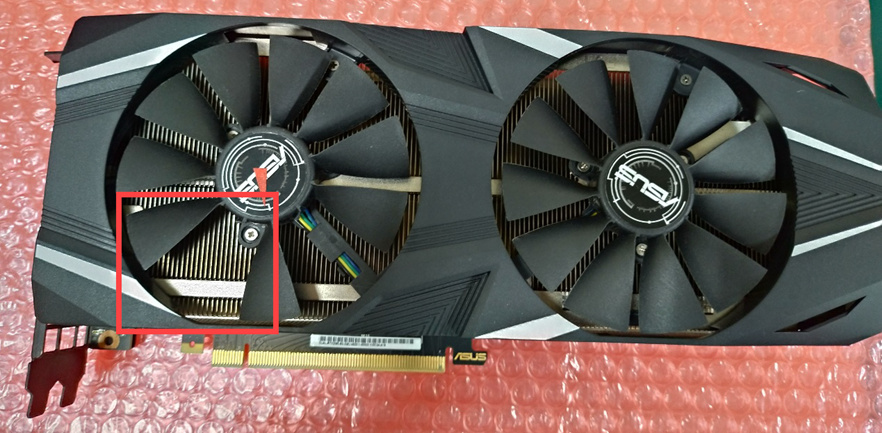


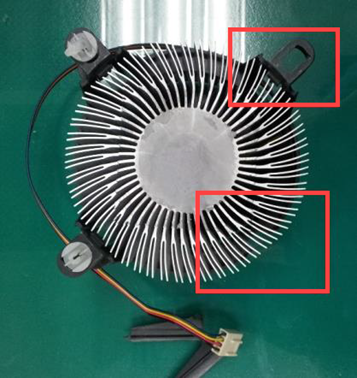
Liquid intrusion or water stains on the thermal module
Outer Surface (Case)
Impact damage or scratches on the outer surface



Dents on the outer surface

Cracks or breakage on the outer surface
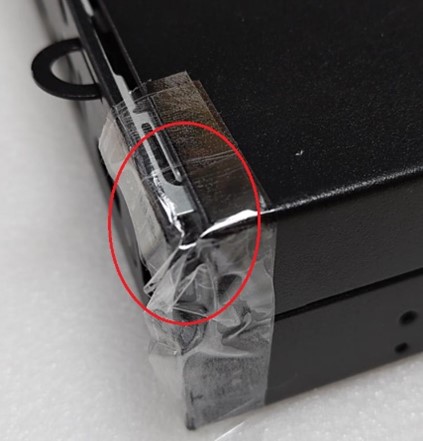


Intrusion of foreign objects, including liquids

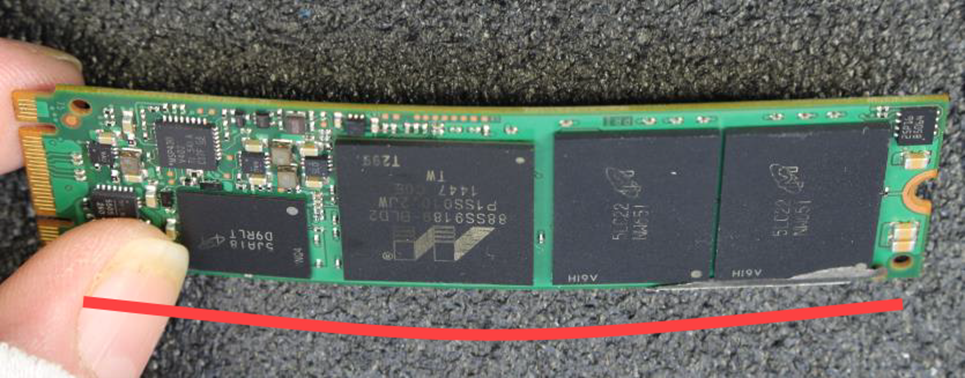
Solid-State Drive(SSD)
Impact damage, deformation, or destruction to the SSD's circuit board, including the gold fingers or pins
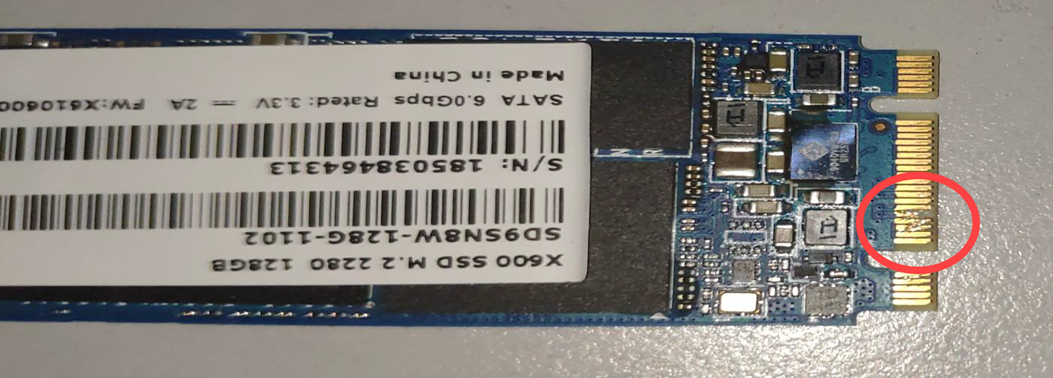
Memory Module
Impact damage, deformation, or destruction to the memory module's circuit board, including the gold fingers or pins

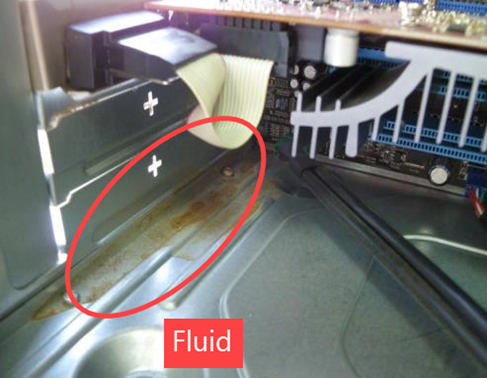
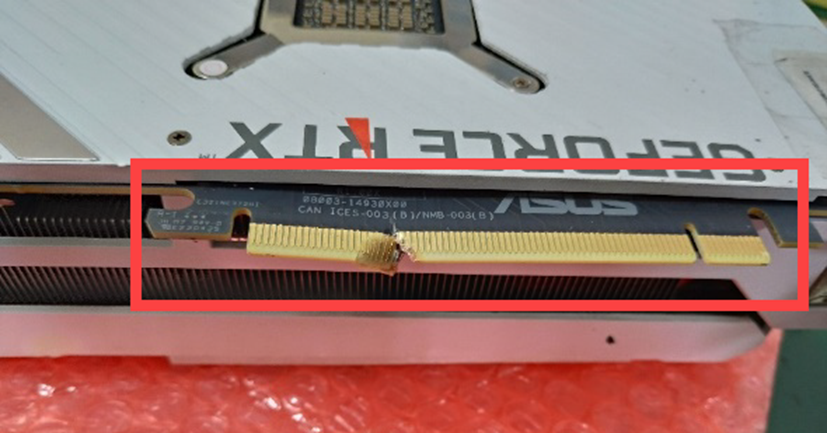
Graphics card
Graphics card circuit board (including the gold fingers or pins) is dented, deformed, or damaged


Hard Drive
Impact damage, deformation, or destruction to the surface of the hard drive




Damage to the hard drive's air-tight pore


Impact damage, deformation, or destruction to the hard drive's circuit board

Impact damage, deformation, or destruction to the hard drive's connector


Loose or worn screws on the hard drive

Use of non-original screws on the hard drive

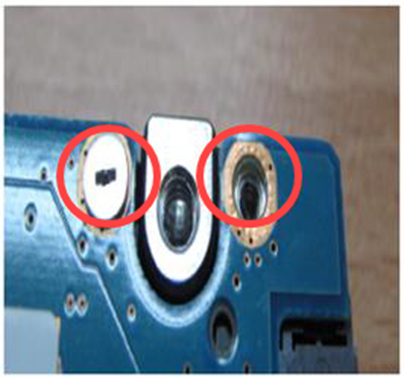
I/O port
Includes all external connection ports such as USB, Ethernet, charging ports, HDMI, DisplayPort, audio jacks, etc.
Breakage or detachment of the plastic flaps (tongue parts) on I/O ports


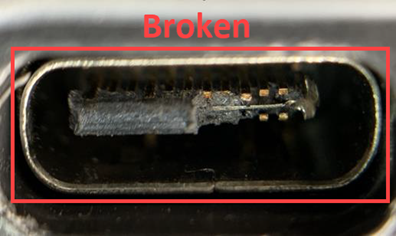
Broken or bent pins on I/O ports


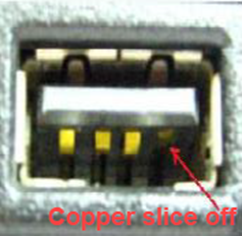
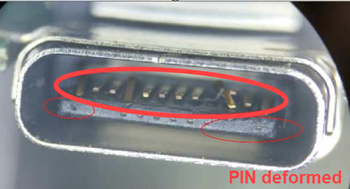
Deformation, cracks, or breakage in the appearance of I/O ports
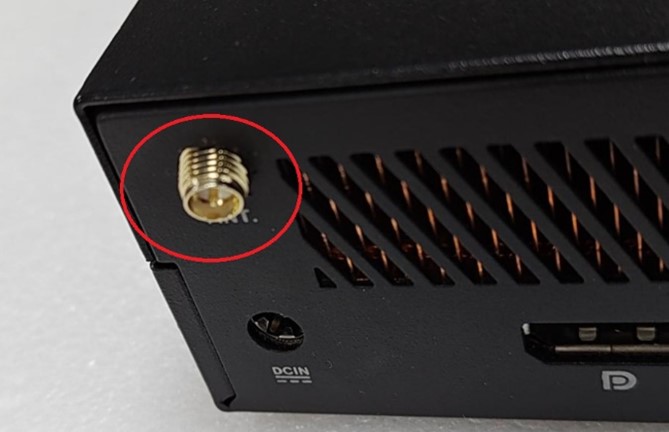
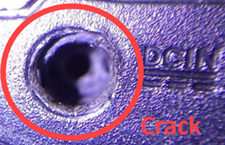



Oxidation of I/O ports