[Wireless Router] What is whole-home mesh WiFi?

A guide to whole-home mesh WiFi networking
What does mesh WiFi mean? How does mesh WiFi work?
What are the benefits of mesh WiFi?
What is the difference between mesh WiFi and traditional routers?
Is mesh WiFi better than extra routers or repeaters?
Can I use a mesh WiFI network with existing routers/ repeaters/ powerline?
Is mesh WiFi faster?
How do I set up a mesh WiFi network?
How much coverage will a mesh WiFi network provide?
Can you have too many mesh nodes? How many do I need?
Does mesh WiFi need a modem?
Does mesh WiFi need Ethernet?
What is mesh WiFi backhaul?
What are dual-band and tri-band mesh WiFi routers? Is tri-band better than dual-band?
What does mesh WiFi mean? How does mesh WiFi work?
Mesh WiFi, or whole-home WiFi, is a single network that’s enabled by the use of multiple hardware devices – typically meaning a single router that connects wirelessly to a number of ‘satellite nodes’. Placed strategically, these nodes work together to form a single network that provides full WiFi coverage. This mesh network provides coverage to every corner of your home, eliminating WiFi dead zones and providing seamless connections everywhere in your home. Connected devices can switch from one mesh node to another smoothly and seamlessly, so the process is unnoticeable — even when streaming a movie, say.
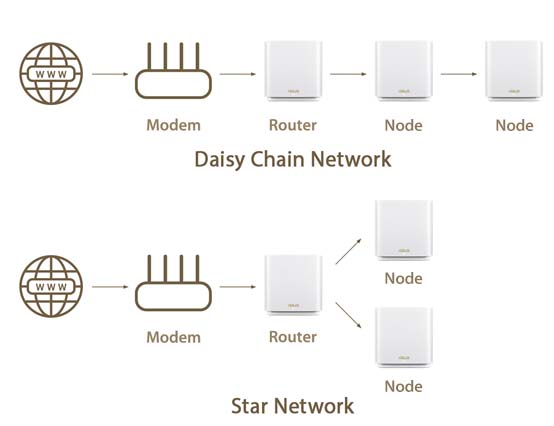
Mesh WiFi typically works with one main router connected to the internet. Additional satellite nodes can be easily added to the network to expand coverage as needed. A mesh WiFi network can use one of two different connection topologies, or logical layouts: star and daisy chain.
Star topology versus daisy-chain topology
The star topology is the most popular choice for a mesh WiFi network, and with good reason. The definition of star topology is that each node is able to connect and communicate directly with the primary router, and also with each other. This brings two distinct advantages. The first is each node’s direct connection with the main router, meaning WiFi signals have just a single ‘hop’ between the node and the router. The second benefit is that if a node should go offline for any reason then the other nodes are able to keep the network operational. In order for star topology to work, the distance between nodes should be greater than the distance between the nodes and the router.
By contrast, daisy-chaining refers to nodes that are connected to one another, in only linear fashion. This means that WiFi signals might have to make multiple hops before they reach a particular device — from the router and then through one or more nodes. This can have the effect of slowing down connections, and can break parts of the network should a particular node develop a problem.
What are the benefits of mesh WiFi?
A good mesh WiFi network will eliminate WiFi dead zones, dropouts and other connectivity issues. This means you’ll enjoy reliable WiFi coverage in every room of your home, and on all floors.
Learn more about ASUS ZenWiFi.
- Wide coverage, stable connectivity
A mesh WiFi system will ensure that you have a strong, stable WiFi connection anywhere in your home. The individual nodes communicate with each other automatically and seamlessly, ensuring you’re able to connect from the loft down to the basement — and anywhere in between.
- A single, flexible home network
Installing a mesh WiFi network eliminates the hassle of switching between different networks in different parts of your home. You just connect to the mesh WiFi network and that’s that — you’ll stay connected everywhere, even if a particular node goes offline or develops a fault. Uniquely, ASUS mesh routers let you choose how you name your WiFi networks: a single name for the entire network, or separate names for each frequency band.
- Easy setup and management
A mesh WiFi network enables simple management of all connections. Specifically, with ASUS routers, the free ASUS Router app lets you complete setup in just few simple steps, with automatic synchronization of all nodes.*
* The auto-synchronization feature is only supported by ASUS ZenWiFi routers.
- Commercial-grade security
With ASUS routers, ASUS AiProtection and Parental Controls is free. This provides total peace of mind, and you can keep an eye on everything that's happening on your network via the mobile app. It also updates itself automatically whenever needed, ensuring the best protection at all times.
*Please check supported routers with AiProtection below. https://www.asus.com/Content/AiProtection
- Smart looks for smart homes
ASUS ZenWiFi works perfectly with smart-home services — such as Alexa skills and Google Assistant — and has a simple and premium design that suits any décor.
*For detailed list of supported routers, please visit the model's webpage.
What is the difference between mesh WiFi and traditional routers?
A traditional router centralizes your home network, while a mesh WiFi system does not. With a traditional setup, every device must make a direct connection to the router as it's the single point of access. The further you and your connected device move away from the router, the weaker the signal will become.
A mesh WiFi network, on the other hand, provides multiple points of access. These nodes interconnect with each other wirelessly to form a single network, automatically switching connected devices to the closest and strongest signal. You can typically add as many nodes as needed to ensure reliable WiFi access around your whole home.

Is mesh WiFi better than extra routers or repeaters?
Comparing mesh WiFi to routers and repeaters is like comparing apples with oranges. Put simply, which is best depends on your needs.
For example, for a single-floor apartment that has heavy and high-traffic internet use, such as gaming, streaming and large data transfers, traditional routers are good choice. The best examples offer powerful performance, fast processing and rich features. Advanced management interfaces and app-based control also make it easy to create custom configurations.
However, if you’re trying to ensure reliable WiFi for a whole house and across two or more floors then a mesh system is often the best choice. Strategic placement of nodes will eliminate WiFi dead zones, so you’ll be able to walk around the whole house and stay connected. Easy set up and management tends to be another selling point for mesh WiFi systems. With the ASUS Router app, for instance, it takes few simple steps to setup a mesh network. So, if you want a hassle-free setup and whole-home coverage, mesh WiFi is the easiest solution.
How to Design the Perfect Mesh Network?
Finally, let's look at repeaters or range extenders. These are certainly effective when it comes to extending the range of a traditional router, and are normally more affordable than a mesh WiFi system. However, WiFi performance can suffer drastically and, depending on the particular make and model, you may be forced to switch networks manually when you wish to switch from the router to the extender.
Can I use a mesh network with existing routers/ repeaters/powerline?
Yes you can. ASUS developed AiMesh, a clever technology that combines the best features of traditional high-end routers and mesh WiFi systems. ASUS routers with AiMesh support can be added into a mesh network without hassle, and it also allows you to mix different WiFi routers to create a mesh network. For those new to ASUS, if you buy an ASUS router and find that later you need to extend coverage, simply add extra AiMesh-compatible ASUS routers to your AiMesh system when you're ready: you're in full control!
Learn more about AiMesh.
Mesh WiFi is not really faster, but goes farther. There are many factors that affect connection speed but it’s fair to say that the biggest benefit of mesh WiFi is range rather than speed. With two or more nodes around your home, you need never be out of range of a WiFi signal. However, if you live in a smaller place, and care more about speed than range, then a single-point router might be the better buy.
With ASUS ZenWiFi and AiMesh routers setup is easy, via the free ASUS Router app.


How much coverage will a mesh WiFi network provide?
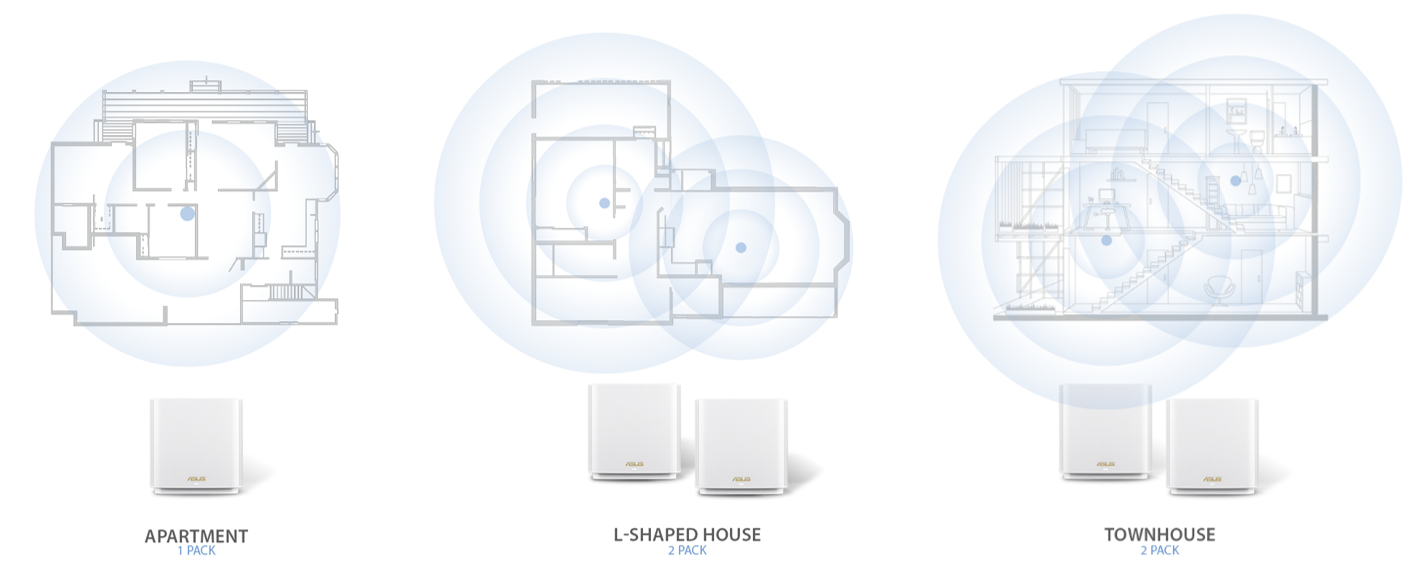
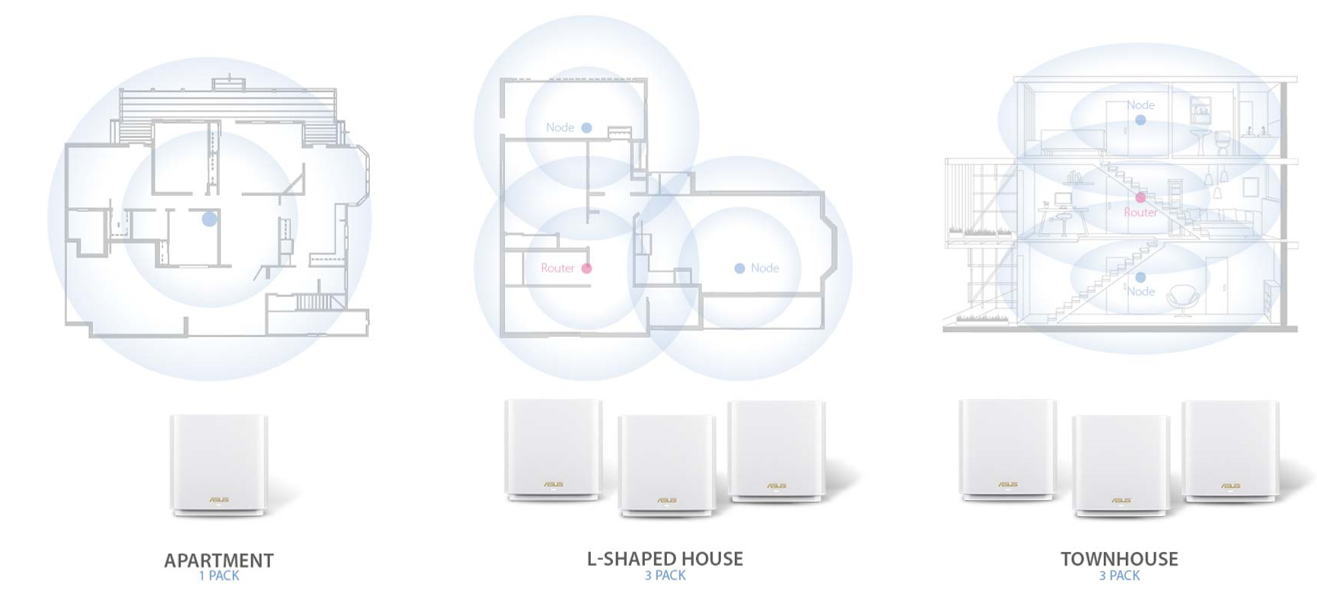
A well-designed mesh network will ensure good WiFi connectivity throughout your home. However, coverage can be affected by a variety of factors – including the distance between nodes and the router, and even materials in your home. For a single mesh WiFi pack, place the hub near the center of the house. For multiple packs, the optimal distance is no more than 10-15 meters between nodes.
Luckily ASUS ZenWiFi can detect the distance to the nearest node, and if it's too far, the LED light will turn yellow. For more about LED color status, please refer to below.
https://www.asus.com/support/FAQ/1044577/
Can you have too many mesh nodes? How many do I need?
Mesh WiFi allows a network to grow to meet to your needs, but more nodes doesn’t always mean better performance. Typically, for whole-home coverage, ASUS ZenWiFi supports a router and up to a maximum of nine nodes for optimal performance with a wireless backhaul.
Yes. ASUS mesh WiFi systems don't have a built-in modem, so you will still need a modem from an internet service provider (ISP) to access the internet.
Mesh routers are designed to connect wirelessly, so no Ethernet is required. However, ASUS mesh WiFi routers do offer Ethernet connectivity, so the choice is yours.If you take dual band models to build mesh WiFi system, we suggest you use Ethernet connectivity.
What is backhaul in mesh WiFi?
Backhaul is a technical term used in mesh WiFi technology. It refers to the underlying data connection between the nodes within a single mesh WiFi system, or between a particular node and the router. This is separate to any device connections on the network. There are generally two backhaul options — a wired Ethernet connection or a wireless connection. A wired Ethernet connection will ensure the best performance but requires more work, as you might need to connect Ethernet cables to every node. Wireless backhaul is obviously simpler, and is typically available on either the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz frequency bands. With the latest WiFi 6E standard coming to market, some mesh systems might use the less-congested 6 GHz band for backhaul.
What are dual-band and tri-band mesh WiFi routers? Is tri-band better than dual-band?
Dual-band routers broadcast WiFi over two separate bands – 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz – to create up to two distinct networks. A traditional tri-band router adds a second 5 GHz band, enabling up to three distinct networks. With the latest WiFi 6E standard, a tri-band router can offer 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz and 6 GHz bands*. A tri-band router is best, because it is able to dedicate a band for backhaul connections – ensuring a stable connection and eliminating performance impacts.
*The WiFi 6E 6GHz frequency band is subject to regulatory approval and may not be available in all countries.